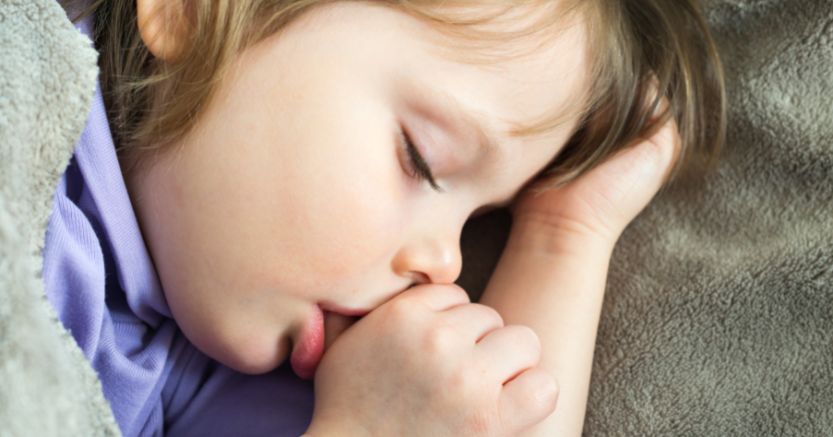
Thumb-sucking is a natural self-soothing behavior for young children, but what if an older child starts or returns to the habit? This often happens as a form of age regression—a temporary response to stress, change, or emotional overwhelm. In this article, we explain why it happens, the potential impacts, and strategies to help your child break the habit safely.
What is Age Regression?
The medical experts at Verywell Health define this occurrence as the reversion of an individual to a younger state of mind. Age regression simply means moving backward in development and is a normal—and often temporary—responsive condition for children.
Why Does Age Regression Occur?
Age regression often appears when a child experiences stress, change, or emotional overwhelm. This may happen during major transitions, such as starting school, welcoming a new sibling, moving to a new home, or even during smaller day-to-day frustrations.
In these moments, returning to familiar behaviors like thumb-sucking helps the child feel secure and comforted. It provides predictability and control while they are still developing more mature coping strategies.
Thumb Sucking as a Soothing Response
Thumb-sucking is one of the earliest self-soothing behaviors children learn. It provides a sense of comfort, safety, and familiarity, especially during moments of stress or transition. When age regression occurs, a child may return to thumb-sucking because it is a coping tool they already know and trust.
There isn’t a specific age when regression may occur. Thumb-sucking simply indicates that a child is trying to cope with something new or overwhelming. However, when the habit continues past about age five, it can begin to affect dental development and emotional growth. At that stage, gently guiding your child toward other soothing strategies can better support their long-term well-being.
The Impacts of Prolonged Thumb Sucking
When thumb and finger sucking continue as a child ages or through age regression, the repeated action can affect oral and dental development.
Over time, this may contribute to:
- Emotional or social discomfort, especially if the child feels self-conscious about the habit
- Changes in bite alignment (overbite, open bite, or crossbite)
- Shifts in jaw growth, which may influence facial structure
- Crowding or spacing issues as adult teeth come in
- Speech difficulties, such as lisps or trouble forming certain sounds
The Best Treatments for Age Regression and Thumb Sucking
If you notice your child continuing to suck their thumb or an older child returning to thumb sucking, it’s important to keep an eye on the factors that may be driving this behavior. Consulting a pediatrician, dentist, or child therapist can help assess the emotional and physical causes as well as assist with creating a treatment plan.
Helpful approaches include:
- Positive encouragement and reassurance
- Creating consistent, calming routines for bedtime and transitions
- Behavioral charts and small rewards
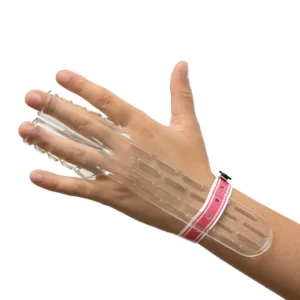
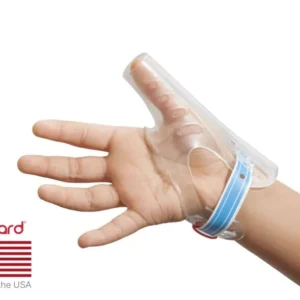
- A gentle habit-breaking device like TGuard’s AeroThumb
Many parents report noticeable improvement in their child’s thumb sucking habit within a week of using the TGuard AeroThumb.
Thumb Sucking and Age Regression FAQ
Why is my child sucking their thumb again?
Children may return to thumb-sucking as a coping mechanism during stress, change, or emotional overwhelm as a source of comfort and security.
What is the link between thumb sucking and age regression?
Thumb-sucking is a common coping mechanism for young children, helping them feel secure and comforted. When an older child begins—or returns to—thumb-sucking, it is often a form of age regression, meaning the child is temporarily reverting to earlier behaviors in response to stress, change, or emotional overwhelm. In these moments, thumb-sucking provides familiarity and reassurance while the child navigates challenges.
What health impacts does thumb sucking cause?
When thumb-sucking continues past age 4–5, especially as part of age regression, it can affect both dental development and overall well-being. Key potential impacts include:
- Dental alignment issues: Overbite, open bite, or crossbite
- Jaw growth changes: Shifts in jaw shape and facial structure
- Tooth crowding or spacing problems as adult teeth emerge
- Speech difficulties: Lisps or trouble forming certain sounds
- Emotional or social effects: Self-consciousness or anxiety about the habit
While thumb-sucking during age regression is often a temporary coping mechanism, early guidance and gentle intervention can help prevent long-term issues while supporting your child’s emotional health.
How can I help my child’s thumb sucking from age regression?
Gentle encouragement, consistent routines, alternative soothing methods, and supportive devices like TGuard AeroThumb can help children break the habit.
Sources:
“Theories About Age Regression and Trauma” from Verywell Health